Almost 300 years later, Benjamin Franklin is the face of the U.S. $100 bill, and it is protected by a myriad of security features including secret images, special ink, hidden watermarks, and magnetic signatures, among others. In this visual, we’ve broken down the $100 bill to showcase the anatomy of American currency.
The Makeup of American Money
There are 6 key features that identify real bills and protect the falsification of American money.
① Serial Numbers & EURion Constellation
The most basic form of security on an $100 bill is the serial number. Every bill has a unique number to record data on its production and keep track of how many individual bills are in circulation. The EURion constellation is star-like grouping of yellow rings near the serial number. It is only detectable by imaging software.
② Color Changing Ink
This ink changes color at different angles thanks to small metallic flakes within the ink itself. The $100 bill, like all other paper bills in the U.S., has its value denoted in color changing ink on the bottom right-hand corner; unlike other bills, it also features a liberty bell image using the ink.
③ Microprinting
Microprinting allows for verifiable images that cannot be scanned by photocopiers or seen by the naked eye. The $100 bill has phrases like “USA 100” written invisibly in multiple places.
④ Intaglio Printing
Rather than regular ink pressed onto the paper, intaglio printing uses magnetic ink and every different bill value has a unique magnetic signature.
⑤ Security Threads & 3D Ribbons
The security thread is a clear, embedded, vertical thread running through the bill. It can only be seen under UV light, contains microprinted text specifying the bill’s value, and on each different bill value it glows a unique color. Additionally, 3D ribbons are placed in the center of $100 bills with a pattern that slightly changes as it moves.
⑥ Paper, Fibers, & Watermarks
Because American money is made of cotton and linen, blue and red cloth fibers are woven into the material as another identifying feature. Finally, watermarks are found on most bills and can only be detected by light passing through the bill.
The Relevance of Cash
Here’s a look at the total number of each paper bill that is physically in circulation in the U.S.: Interestingly, a number of $500-$10,000 dollar bills are in someone’s pockets. And while they are not issued anymore, the Fed still recognizes the originals of these bills that were legally put into circulation in the past.
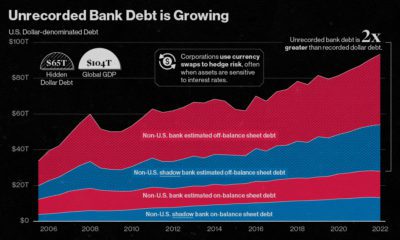
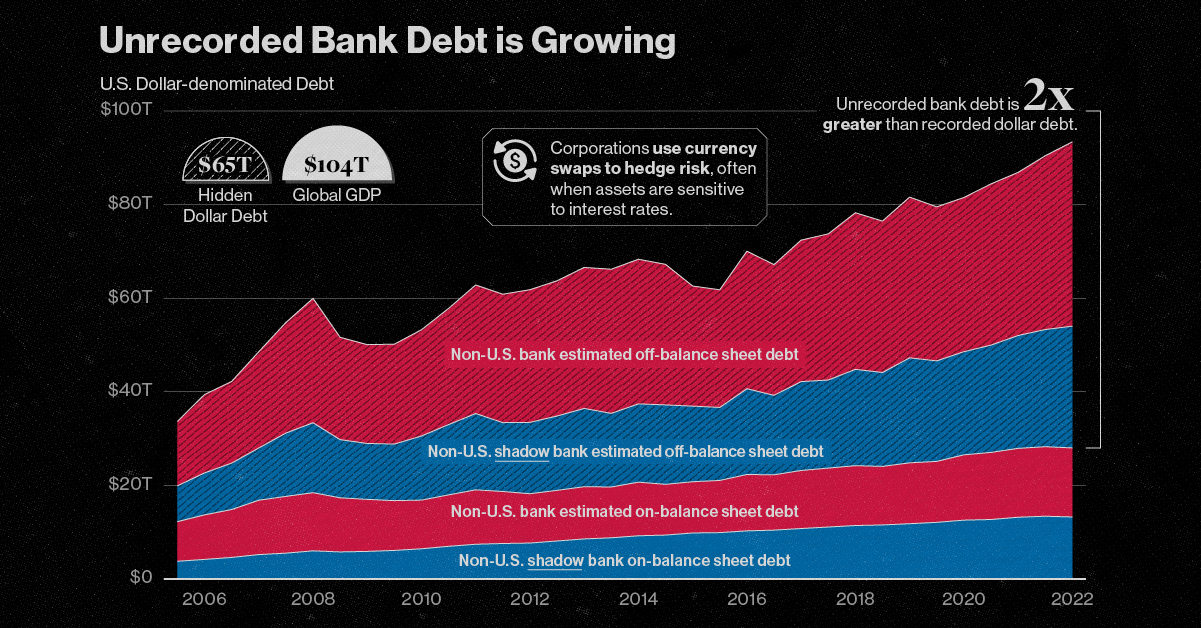
Additionally, there is fake money passing hands in the U.S. economy. Being the most widely-accepted currency in the world, it’s no wonder many try to falsely replicate American money. According to the U.S. Department of Treasury, there are approximately $70 million in counterfeit bills currently circulating in the country. Finally, a natural question arises: how many people still use cash anyways? Well, a study from Pew Research Center found that it while it is a dwindling share of the population, around 58% of people still use cash for some to all of their weekly purchases, down from 70% in 2018 and 75% in 2015. on The scale of hidden dollar debt around the world is huge. No less than $65 trillion in unrecorded dollar debt circulates across the global financial system in non-U.S. banks and shadow banks. To put in perspective, global GDP sits at $104 trillion. This dollar debt is in the form of foreign-exchange swaps, which have exploded over the last decade due to years of monetary easing and ultra-low interest rates, as investors searched for higher yields. Today, unrecorded debt from these foreign-exchange swaps is worth more than double the dollar debt officially recorded on balance sheets across these institutions. Based on analysis from the Bank of International Settlements (BIS), the above infographic charts the rise in hidden dollar debt across non-U.S. financial institutions and examines the wider implications of its growth.
Dollar Debt: A Beginners Guide
To start, we will briefly look at the role of foreign-exchange (forex) swaps in the global economy. The forex market is the largest in the world by a long stretch, with trillions traded daily. Some of the key players that use foreign-exchange swaps are:
Corporations Financial institutions Central banks
To understand forex swaps is to look at the role of currency risk. As we have seen in 2022, the U.S. dollar has been on a tear. When this happens, it hurts company earnings that generate revenue across borders. That’s because they earn revenue in foreign currencies (which have likely declined in value against the dollar) but end up converting earnings to U.S. dollars. In order to reduce currency risk, market participants will buy forex swaps. Here, two parties agree to exchange one currency for another. In short, this helps protect the company from unfavorable foreign exchange rates. What’s more, due to accounting rules, forex swaps are often unrecorded on balance sheets, and as a result are quite opaque.
A Mountain of Debt
Since 2008, the value of this opaque, unrecorded dollar debt has nearly doubled.
*As of June 30, 2022
Driving its rise in part was an era of rock-bottom interest rates globally. As investors sought out higher returns, they took on greater leverage—and forex swaps are one example of this.
Now, as interest rates have been rising, forex swaps have increased amid higher market volatility as investors look to hedge currency risk. This appears in both non-U.S. banks and non-U.S. shadow banks, which are unregulated financial intermediaries.
Overall, the value of unrecorded debt is staggering. An estimated $39 trillion is held by non-U.S. banks along with $26 trillion in overseas shadow banks around the world.
Past Case Studies
Why does the massive growth in dollar debt present risks? During the market crashes of 2008 and 2020, forex swaps faced a funding squeeze. To borrow U.S. dollars, market participants had to pay high rates. A lot of this hinged on the impact of extreme volatility on these swaps, putting pressure on funding rates. Here are two examples of how volatility can heighten risk in the forex market:
Exchange-rate volatility: Sharp swings in USD can spur a liquidity crunch U.S. interest-rate volatility: Sudden rate fluctuations can mean much higher costs for these trades
In both cases, the U.S. central bank had to step in to provide liquidity in the market and prevent dollar shortages. This was done through pumping cash into the system and creating swap lines with other non-U.S. banks such as the Bank of Canada or the Bank of Japan. These were designed to protect from declining currency values and a liquidity crunch.
Dollar Debt: The Wider Implications
The risk from growing dollar debt and these swap lines arises when a non-U.S. bank or shadow bank may not be able to hold up their end of the agreement. In fact, on a daily basis, there is an estimated $2.2 trillion in forex swaps exposed to settlement risk. Given its vast scale, this dollar debt could have greater systemic spillover effects. If participants fail to pay it could undermine financial market stability. Because demand for U.S. dollars increases during market uncertainty, a worsening economic climate could potentially expose the forex market to more vulnerabilities.